Tsunami Models Help Scientists Forecast Which of the Following
Science of Predicting Monster Waves. The lesson is intended for Weather Forecast Office staff particularly National Weather Service Warning Coordination Meteorologists who desire a better understanding of tsunamis in their role as issuers of tsunami warning-related messages.
Tsunami S Top Model Science Of Predicting Monster Waves Live Science
The objective of tsunami modeling research is to develop numerical models for faster and more reliable forecasts of tsunamis propagating through the ocean and striking coastal communities.
. Forecast products include estimates of tsunami amplitudes flow velocities and arrival times for offshore coastal and inundation areas. 13Which of the following are potential long term effects of subduction zone earthquakes and their associated. The simulations were done for off New.
Tsunamis Top Model. Vertical seafloor displacement of 10m. In a companion paper published in Pure and Applied Geophysics scientists report that when they used the new energy estimate in tsunami.
12Tsunami models help scientists forecast which of the following. Scientists at The University of Texas at Austin have begun a federal funded international project that wants to minimize future disasters by making earthquake forecasts a reality. A series of numerical experiments were Kain et al.
In 2010 society had better tsunami-warning technology than in 1960. 1861 w mag 85 2000 w mag 79 2004 sumatra indonesia. Help scientists forecast wave height and arrival times.
They allow to transmit up to 98 percent of data and to measure tsunamis with the amplitude of less than one centimeter. The 1964 Alaska Tsunami. Forecasts by learning from this tsunami.
Tsunami Modeling and Research. Megathrust earthquake mag 9 epicenter 250km offshore hypocenter 10km under seafloor rupture. Tsunami models help scientists forecast which of the following.
A digital elevation model DEM image for the Society Islands French Polynesia in the South Pacific. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. To help identify and predict the size of a tsunami scientists look at the size and type of the underwater earthquake that precedes it.
You highlight in a News story the controversy over the reliance of tsunami early-warning systems on model-based forecasts Nature 464 1415. Prior to this tsunami no entity had tsunami warning responsibilities for the Indian Ocean and no numerical models existed to forewarn populations of the expected impact. The 2004 tsunami led to greater global cooperation and improved techniques for detecting waves that could reach faraway shores even though scientists still cannot predict when an earthquake will strike.
A year later scientists and emergency managers are still struggling to improve their tsunami detection and warning systems before the ocean strikes again. Arrival times Wave height Earthquake magnitudes Fatalities. A deep earthquake A shallow earthquake A short duration rupture A long duration rupture Question 3 of 20 4 points Tsunami models help scientists forecast which of the following.
With documented cases of tsunami-generating landslides in Alaska. But it will also benefit anyone wanting to learn more about how tsunamis work including emergency. The study the first to estimate total energy of a tsunami from measurements made in real time during the tsunami propagation was published earlier this month in the Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans.
The 1960 Chile Tsunami. If a tsunami is detected the warning centers run tsunami forecast models developed by NOAAs Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory and the warning centers. Choose all that apply.
First they use an ocean-wide propagation model to advance the tsunami energy from the source to the coastal margin. 11 sent a. In May of 2020 local geologists identified a steep unstable slope that has the potential to become a tsunami-generating landslide in Barry Arm a glacial fjord 60 miles east of Anchorage Alaska.
NOAA The 89-magnitude earthquake that struck Japan last Friday Mar. A decade ago scientists did not have a tsunami warning system in place in the Indian Ocean because there had been no recent history of tsunamis there. 1797 w mag 84 and 1833 w mag 87.
These models use real-time information from the observation systems and pre-established scenarios to simulate tsunami movement across the ocean and estimate coastal impacts including wave height and arrival. 2010Important advances have been made in near. The primary responsibility of the NOAA Center for Tsunami Research NCTR is to provide assistance to the Tsunami Warning Centers TWC in.
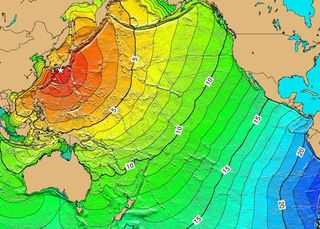
A SIFT forecast is the numerical estimate of amplitude travel time and additional tsunami properties using an inundation model constrained by real-time tsunami observations for specific coastal locations. A map of estimated tsunami travel times. Choose all that apply.
This information is not always helpful however because a tsunami can. Earthquake Forecasts Move a Step Closer to Reality. In parallel with developing the DART buoy PMEL scientists created tsunami forecast models to use the data provided by the buoys to forecast a tsunamis impact at specific locations.
Japan will soon start to install a 32. 12Tsunami models help scientists forecast which of the following. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
Long-term effects of subduction zone earthquakes. The 1998 Papua New Guinea Tsunami. March 7 2017.
The 1960 Chile Tsunami. Similarly waves following the first one known as trailing waves made post-tsunami rescue efforts in 2010 life-threatening. YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE.
2020 investigate the potential impact provided by the authors to demonstrate the differ- at Hobart Airport and nearby coastal communities ences between tsunami models using static or from a tsunami along the Puysegur subduction zone dynamic tide inputs. The Science Behind Tsunami Detection. Simulations have since been created to accurately estimate damage and were tested successfully in the weeks following the tsunami.
The 1998 Papua New Guinea Tsunami. Choose all that apply. 13Which of the following are potential long term effects of subduction zone earthquakes and their associated.
The 1964 Alaska Tsunami. Tsunamis huge ocean waves generated by sudden movements in the seafloor landslides or volcanic. Once the first tsunami data becomes available it should be processed quickly and accurately with the help of mathematical models the forecast should be made and people should be warned about possible danger.
Who are the experts. NOAA bathymetric data helps scientists more accurately model tsunami risk within Barry Arm. This DEM was built for the NOAA Tsunami Warning Centers to aid in forecasting throughout the Pacific Basin.
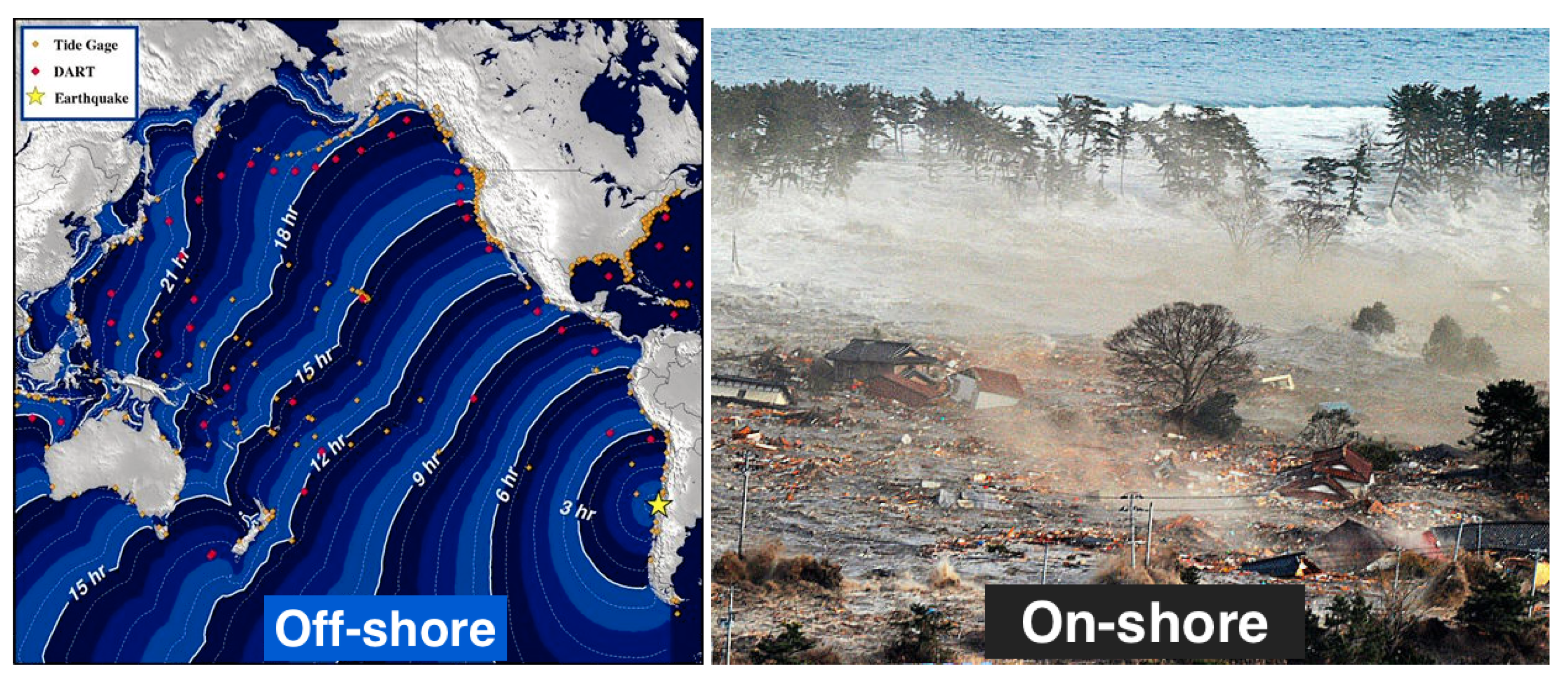
Choose all that apply. Choose all that apply. A damaged house following the Tohoku earthquake and tsunami that devastated Japan in 2011.
This is often the first information they receive because seismic waves travel faster than tsunamis. Fatalities Arrival times Earthquake magnitudes Wave height Question 4 of 20 6 points Here are two hypothetical earthquakes.
Tsunami Forecasting Pacific Tsunami Museum

Human Driven Climate Change Sent Pacific Northwest Temperatures Soaring Climate Change Nature Climate Change Atmospheric Circulation

Video Clip Dr Mike Spearpoint From The University Of Canterbury Describes How Computer Modelling Is Used To Predict What Might H Used Computers Model Dr Mike

Scientists Make Strides In Tsunami Warning Since 2004

Scientists Make Strides In Tsunami Warning Since 2004

Japan S Coastline Before And After The Tsunami Japan Earthquake Earthquake Tsunami

T T Weather Central A Lengthy But Very Interesting Read Via Space Com 𝗜𝗻𝘃𝗶𝘀𝗶𝗯𝗹𝗲 𝗲𝗮𝗿𝘁𝗵𝗾𝘂𝗮𝗸𝗲 𝗰𝗮𝘂𝘀𝗲𝗱 𝗺𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗿𝗶𝗼𝘂𝘀 𝟮𝟬𝟮𝟭 𝘁𝘀𝘂𝗻𝗮𝗺𝗶 𝘀𝗰𝗶𝗲𝗻𝘁𝗶𝘀𝘁𝘀 𝗳𝗶𝗻𝗱 The Mysterious Source Of A Globe Spanning

Saildrone Is A Wind And Solar Powered Autonomous Boat Collecting Live Data Anywhere In The Ocean Saildrones Can Travel Autonomously R Model Boats Boat Ocean

Tsunamis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Waves Tides And Tsunamis Let S Talk Science

Noaa Scientists Able To Measure Tsunami Height From Space India Reliefweb

Scientists Investigate How To Defend Europe Against Tsunamis Research And Innovation
Earthquake Depth Impacts Potential Tsunami Th Eurekalert

Tsunami Hitting Shore Tsunami Waves Tsunami Science Lessons

Tsunami Forecast Model Tsunami Japan Earthquake Tsunami Waves
Geosciences Free Full Text Modeling And Simulation Of Tsunami Impact A Short Review Of Recent Advances And Future Challenges Html

Scientists Accurately Predict Path Of Tsunamis But Still Uncertain About Impacts The Mercury News

Natural Disaster Project 1st Grade Natural Disasters Activities Natural Disasters Teaching Weather
Comments
Post a Comment